Olive oil, a key ingredient in Mediterranean cuisine and prized for its health benefits, is a staple cooking oil that has gained popularity worldwide. Known for its unique flavor, health benefits, and versatile uses, olive oil is widely used in cooking, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals. However, the price of olive oil can fluctuate due to factors such as climate conditions, agricultural challenges, demand dynamics, and geopolitical events. This article provides an in-depth look at historical olive oil price trend, the factors influencing these trends, and the future outlook for the global olive oil market.
1. Overview of Olive Oil and Its Production
1.1 What is Olive Oil?
Olive oil is extracted from olives, the fruit of the olive tree (Olea europaea). Olive oil production involves pressing and crushing olives, followed by mechanical extraction to produce various grades of oil. Common types include:
- Extra Virgin Olive Oil (EVOO): The highest quality, cold-pressed oil that retains most of the olives’ flavor and health benefits.
- Virgin Olive Oil: Similar to EVOO but with slightly higher acidity, making it slightly less refined.
- Refined Olive Oil: Chemically treated to remove impurities, often blended with virgin olive oil to improve flavor.
- Pomace Olive Oil: Extracted from the olive residue left after pressing, usually by chemical solvents.
Enquire For Regular Prices: https://www.procurementresource.com/resource-center/olive-oil-price-trends/pricerequest
1.2 Major Olive Oil-Producing Regions
The Mediterranean region dominates global olive oil production, with Spain, Italy, and Greece as the largest producers. Together, these countries account for over 70% of worldwide production. Other significant producers include Turkey, Tunisia, and Portugal, while smaller-scale production is found in countries like the United States, Argentina, and Australia.
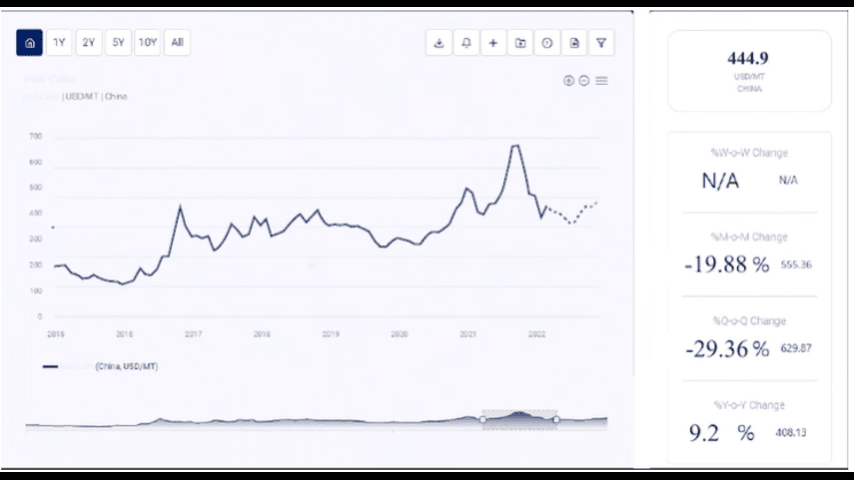
2. Historical Olive Oil Price Trends
2.1 2000 to 2010
Between 2000 and 2010, olive oil prices experienced moderate fluctuations primarily due to demand growth and weather conditions:
- Rising Global Demand: The popularity of the Mediterranean diet and increased consumer awareness of olive oil’s health benefits contributed to steady demand growth, particularly in North America and parts of Asia.
- Weather-Related Production Challenges: Unpredictable weather events, such as droughts or frosts, periodically affected harvests in major producing countries, leading to temporary price spikes.
During this period, olive oil prices remained stable on average, though they saw seasonal increases due to factors such as poor weather and increased demand.
2.2 2011 to 2016
From 2011 to 2016, olive oil prices experienced greater volatility due to multiple factors:
- Pest Infestations and Crop Diseases: In Italy, the Xylella fastidiosa bacterium and olive fruit fly infestations severely impacted olive trees, reducing crop yields and driving up prices.
- Economic and Environmental Pressures: Economic challenges in Europe and adverse weather conditions in Spain and Greece led to production fluctuations, contributing to price volatility.
- Increased Export Demand: Rising exports to countries outside the Mediterranean, such as the United States and China, also placed pressure on supply, leading to price increases.
During these years, olive oil prices fluctuated more dramatically, with significant price increases during years with substantial production losses due to pests and weather events.
2.3 2017 to 2019
Between 2017 and 2019, olive oil prices experienced stabilization, though occasional disruptions impacted prices:
- Improved Harvests in Spain: Favorable weather conditions in Spain, the largest producer, led to more abundant yields and stabilized supply levels, helping to moderate prices.
- Steady Demand Growth: Global demand continued to increase as consumers in the U.S., Canada, and parts of Asia incorporated olive oil into their diets.
- Regulatory Changes: The European Union implemented new regulations and quality control measures, which affected production costs and export practices. These changes helped improve quality standards and supported higher prices for premium olive oils.
Prices remained relatively stable during this period, with moderate fluctuations due to weather changes and shifts in demand.
2.4 2020 to Present
Since 2020, olive oil prices have shown increased volatility due to factors such as the COVID-19 pandemic, extreme weather events, and economic uncertainties:
- COVID-19 Demand Surge: The pandemic led to a spike in home cooking, which boosted demand for olive oil. This increase, combined with initial supply disruptions, caused prices to rise in early 2020.
- Adverse Weather Conditions: Droughts in key producing regions like Spain and Italy in 2021 and 2022 severely impacted olive harvests, reducing supply and pushing prices higher.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Global supply chain challenges led to delays and increased transportation costs, further contributing to higher olive oil prices.
- Geopolitical Factors: Economic sanctions and trade restrictions, especially in the Mediterranean region, have also affected prices by limiting supply channels and increasing production costs.
As of 2023, olive oil prices remain high due to ongoing weather challenges, sustained demand, and rising production and transportation costs.
3. Factors Influencing Olive Oil Prices
3.1 Climate and Weather Conditions
Weather significantly impacts olive oil production:
- Droughts and Extreme Temperatures: Olive trees are highly sensitive to drought and temperature extremes. Severe droughts can drastically reduce yields, resulting in reduced supply and higher prices.
- Frost and Hailstorms: Sudden temperature drops or severe storms during critical growing periods can damage crops, leading to lower production and price spikes.
- Climate Change: As climate change brings more frequent and intense weather events, olive oil-producing regions face increased challenges in maintaining stable yields.
3.2 Pests and Crop Diseases
Olive oil production is vulnerable to pests and diseases that can devastate olive trees:
- Xylella fastidiosa Bacterium: This bacterium has severely impacted Italian olive trees, reducing production capacity.
- Olive Fruit Fly: A common pest in Mediterranean countries, this fly damages olives, reducing yield and quality. Outbreaks require pest control measures that can raise production costs and affect prices.
3.3 Global Demand and Consumer Preferences
Global demand for olive oil has steadily increased due to its health benefits and culinary versatility:
- Health Trends: As consumers prioritize healthier diets, demand for olive oil has grown in markets like North America and Asia, where awareness of its health benefits is rising.
- Expanding Markets: Although Europe remains the largest consumer, demand is growing in non-traditional markets like China, India, and Latin America, driven by rising incomes and interest in international cuisines.
3.4 Trade Policies and Currency Exchange Rates
As a globally traded commodity, olive oil prices are affected by currency fluctuations and trade policies:
- Euro Exchange Rate: Since most olive oil is produced in Europe, the strength of the euro relative to other currencies can impact prices for international buyers. A stronger euro makes European olive oil more expensive in other markets.
- Tariffs and Trade Barriers: Trade restrictions, such as tariffs on EU exports, can increase costs for consumers in importing countries, as seen with U.S. tariffs on European agricultural products in 2019.
3.5 Production and Labor Costs
Production and labor costs, especially in traditional olive oil-producing countries, influence prices:
- Labor-Intensive Harvesting: High-quality olive oil, like extra virgin olive oil, is often hand-harvested, making labor costs a significant part of production expenses. Labor shortages and increased wages can further drive up costs.
- Environmental and Quality Certifications: Meeting organic and quality standards may add to production costs, but it also allows producers to charge premium prices, especially in markets that prioritize sustainability.
4. Future Outlook for Olive Oil Prices
The future of olive oil prices will depend on a range of factors:
4.1 Impact of Climate Change on Olive Harvests
Climate change is expected to present ongoing challenges for olive growers. Rising temperatures and unpredictable rainfall patterns may continue to reduce yields, contributing to long-term price increases. Investment in climate-resilient farming practices may help sustain production but could also raise costs.
4.2 Growing Demand for Organic and Sustainable Products
As more consumers seek sustainably produced food, demand for certified organic and sustainably sourced olive oil is expected to increase. This trend will likely support price growth, especially for high-quality and premium olive oils.
4.3 Expanding Global Markets
New and growing markets in Asia, Latin America, and Africa are expected to support demand for olive oil. As rising incomes and awareness of health benefits drive consumption in these regions, overall demand may continue to grow, sustaining or increasing prices.
4.4 Advances in Production and Technology
Technological innovations in olive farming and production, such as precision agriculture, pest-resistant olive varieties, and water conservation techniques, may help mitigate some production challenges over time. These advancements can contribute to more stable production and reduced price volatility.
Contact Us:
Company Name: Procurement Resource
Contact Person: Leo Frank
Email: sales@procurementresource.com
Toll-Free Number: USA & Canada — Phone no: +1 307 363 1045 | UK — Phone no: +44 7537 132103 | Asia-Pacific (APAC) — Phone no: +91 1203185500
Address: 30 North Gould Street, Sheridan, WY 82801, USA